Rosacea Types, Stages & Symptoms
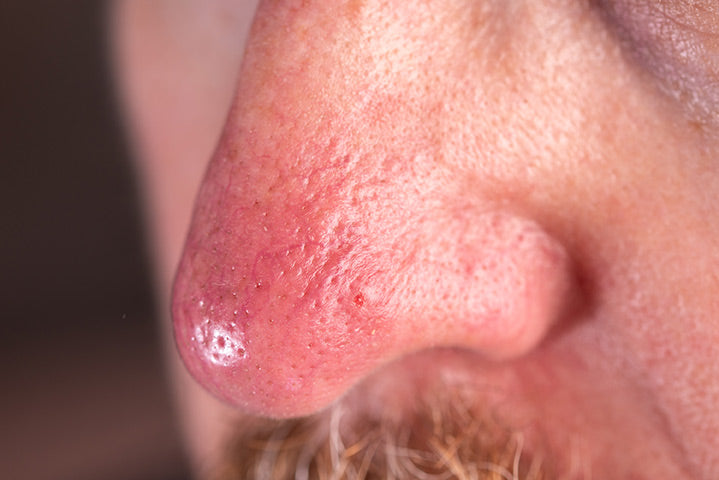
Rosacea symptoms consist of facial redness, spidery veins and rosacea papules that normally progress to a more severe stage unless properly treated.
Rosacea Stages
Rosacea Progresses over time: The facial redness begins and gradually becomes more persistent with spidery blood vessels (telangiectasis) becoming progressively prominent on the nose and cheeks. Trauma from treatments involving abrasives and peeling agents (Retin – A and all other retinoid, steroids, and exfoliants including anti-aging treatment products) easily cause more long-lasting redness. Inflammatory papules (without pus) and pustules (with pus) develop and continue to worsen. Facial pores often become larger and more prominent. If there has been much sun exposure damage over the years, the skin becomes more leathery skin becomes more wrinkled as it is not elastic or as soft to bend. Eventually, the sides of the neck as well as the area down to the center of the chest began to redden and later the ears and area behind the ears also become redder. The facial skin contours gradually become coarse and thickened. A small number of patients realize they have a more serious presentation of the disease with the condition of nose tissue hyperplasia beginning. Hypergenesis is a general term referring to the proliferation of cells within an organ or tissue beyond that which is ordinarily seen as is indicative of cancer cells expansion. “Rosacea is more than a red face” as patients often have symptoms of allergy and sinus problems, fibromyalgia, digestive system disorders, and in later years, osteoporosis and arthritis – rheumatism presents itself along with a lowering of the total immune system. As you read our new rosacea research facts page, you will find that rosacea is just one symptom of a “metabolic acidosis” disorder. Your symptoms will be improved by the use of Rosacea-Ltd IV.
It is often the cumulative effect of the treatments you’ve been using that may actually be the aggravating source or factor of your current treatment. Improving the skin involves a complete change in your thought processes and your approach to treating your facial skin condition. Bass & Boney Pharmaceuticals, Inc. researchers know that total skin care and treatment involves much more than treating the symptoms of damage that has already occurred. Effective rosacea treatment and skin care also involves preventive skin care. The use of sun screens is just one of these preventive skin care treatment measures.
For some people with rosacea, no matter what they try to treat their rosacea symptoms, their skin does not seem to respond. In these cases, one may find that their rosacea is caused by an internal micro-organism imbalance.
Many patients have been frustrated for many years with unsuccessful or marginal results from many rosacea treatments. Antibiotics, retinoid, Accutane, and steroids have been a mainstay of rosacea treatment for years. Patients have noticed that these prescribed treatments and various laser treatments have not worked well as a skin care treatment; also these past treatments may have caused additional damage to the already sensitive skin. Oral and topical antibiotic treatments for adult acne rosacea can work for up to several months before the bacteria become immune to the antibiotic treatment, causing the antibiotic to lose its effectiveness. Oral antibiotic treatments actually cause more symptoms of facial redness. For information on the latest FDA findings, see Bacterial Resistance to Antibiotics.
The different stages or degrees of ocular involvement can dictate the course of treatment of ocular rosacea.
Stage one or mild ocular rosacea encompasses the occasional sensations of dryness of the eyes, or itching of the eyes that comes and goes. Symptoms will also include redness of the eyes. At this stage of eye involvement, treatment may include changing one’s eye makeup or contact lens solution and cleaner – in some cases at this stage this may be all that is needed to provide relief of the milder symptoms of ocular rosacea. Treatment would also include increasing your water intake to add much needed moisture to the eyes.
Stage two or moderate ocular rosacea consists of symptoms that may last a week or more at a time. The symptoms of eye rosacea at this stage may also symptoms that indicate a possible allergy component with ocular rosacea. During this stage, the redness may result in a burning sensation in the eyes; the eyes may feel gritty as if there was something in eye causing irritation. There may be some crusting of the eyelids upon waking in the morning. Treatment of the crusting of the eyelids can be accomplished in one of two ways – some find that just a warm clean wash cloth applied to the eyes for a few minutes is sufficient to loosen and remove the crusting, while others get the best results using the warm clean wash cloth with a drop or two of baby shampoo to be more effective. Treatment options at this stage may involve the consideration of a prescription to relieve dry eyes but be aware that these products can have the added side effect of causing increased burning and eye irritation.
In stage three or severe ocular rosacea, the redness, crusting and dryness are more constant, reoccur more frequently and can last for months at a time. It is at this point that one needs to be more concerned about the possibility of permanent damage to the eyes.
Papulopustular Rosacea – or subtype two rosacea – is characterized by small red bumps and pus-filled acne like pimples. Papulopustular Rosacea is frequently mistaken for acne due to its resemblance to acne. It may also be referred to as acne rosacea. Papulopustular Rosacea is a chronic inflammation of the sweat glands and hair follicles of the central areas of the face. Papulopustular Rosacea may be associated with the involvement of the symptoms of ocular rosacea.
The circulatory network of the skin is extensive and the capillaries are the smallest, most delicate vessels. During normal blood circulation the capillaries undergo constant changes. In between beats the pressure is relieved and the vessels constrict back to their normal size. This return to normal size is accomplished by the natural elasticity in the structure of the capillary. If telangiectasis (spider veins) is present, the capillaries’ elasticity is deteriorated so they remain slightly dilated. The constant influx of blood perpetuates this slight dilation. The skin gradually becomes congested and eventually the capillaries become visible through the skin’s surface. When it comes to telangiectasis, sometimes a person’s lifestyle and habits can be the skin’s worst enemy. In a fair, delicate skin predisposed to telangiectasis, a steady diet of hot, spicy food, chronic alcohol consumption, and eating meals too quickly will promote telangiectasis. Many retinoids used for acne treatment as well as strong or harsh deodorant soaps continue to aggravate the skin resulting in an increase in redness.




Rosacea-LTD
Rosacea-Ltd IV
Share







